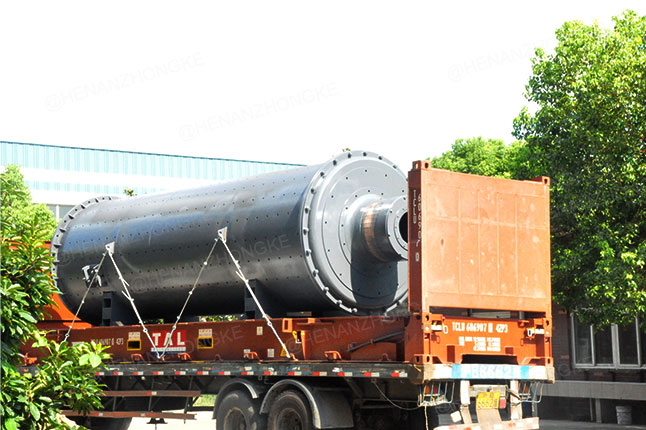
rinding ball mills are fundamental industrial workhorses used to grind and blend materials into fine powders. They are essential in mining for processing ores, in cement production for creating clinker, in paints and coatings for achieving smooth textures, and in chemicals and pharmaceuticals for ensuring precise particle size and reactivity.
Walk through any major industrial plant, and you’ll likely find a piece of equipment that is both simple in concept and critical in function: the grinding ball mill. These cylindrical chambers, filled with grinding media like steel or ceramic balls, are the cornerstone of material size reduction. But which industries rely on this powerful technology to create the products we use every day?
In this article, we’ll explore the key industries that depend on ball mills, breaking down their specific applications and why this technology is so indispensable.
How Does a Ball Mill Work?
Before diving into the industries, it's helpful to understand the basic principle. A ball mill is a rotating cylinder that is partially filled with grinding media (balls). The material to be ground is fed into the cylinder, and as it rotates, the balls cascade and impact the material, crushing and grinding it into a fine powder. The fineness of the final product can be controlled by factors like the rotation speed, the size and material of the balls, and the grinding time.
1. Mining and Mineral Processing
This is arguably the most well-known application for industrial ball mills. The extraction of valuable metals from ore would be nearly impossible without them.
Application: Grinding raw ore into a fine powder to liberate valuable minerals from the surrounding waste rock (gangue). This powdered ore is then ready for separation processes like flotation or leaching.
Why Ball Mills? They are robust enough to handle extremely hard and abrasive ores like copper, gold, iron ore, and nickel. Their ability to achieve a very fine grind is crucial for maximizing mineral recovery rates.
Example: A copper mine uses a large ball mill to grind copper ore to a consistency finer than sand, allowing the copper sulfide particles to be separated efficiently.
2. Cement and Construction Materials
The modern skyline is built, quite literally, with the help of ball mills. They are at the heart of cement production.
Application: Grinding the key ingredient clinker (produced by heating limestone and clay) into the fine powder we know as cement. Ball mills are also used to grind raw materials before they are heated in the kiln.
Why Ball Mills? They provide a consistent and controllable grind, which is essential for the chemical properties and strength of the final cement product. They can also operate in either a dry or wet mode, offering flexibility.
Example: In a cement plant, a ball mill grinds hard clinker nodules along with a small amount of gypsum to create the homogeneous powder packaged as Portland cement.
3. Paints, Coatings, and Dyes
The smooth, even finish of a painted wall or a car's coating is thanks to the precision grinding of ball mills.
Application: Dispersing pigments within a liquid base (vehicle) to create a uniform color, texture, and consistency. This process ensures the paint covers evenly and has the desired gloss and durability.
Why Ball Mills? They excel at de-agglomerating pigment particles and distributing them evenly throughout the mixture. This is critical for achieving color strength, stability, and a smooth application.
Example: A paint manufacturer uses a ball mill to grind titanium dioxide (a white pigment) and other colorants into a resin base to create a high-quality, long-lasting interior paint.
4. Chemicals and Pharmaceuticals
In industries where precision is paramount, ball mills play a vital role in ensuring product quality and efficacy.
Application: Reducing the particle size of chemical compounds and active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs). A smaller, more uniform particle size increases the surface area, which can enhance chemical reactivity, dissolution rates, and bioavailability of drugs.
Why Ball Mills? They offer a sterile and controllable environment for grinding sensitive materials. Ceramic-lined mills and ceramic grinding media are often used to prevent contamination.
Example: A pharmaceutical company uses a small, high-precision ball mill to grind an active drug compound, ensuring it will dissolve quickly and effectively in a patient's bloodstream.
5. Ceramics and Glass Manufacturing
From fine china to advanced technical ceramics, ball mills are used to create the raw material blends.
Application: Grinding and mixing materials like silica sand, feldspar, and clay (kaolin) into a fine, homogeneous "slip" or powder before shaping and firing.
Why Ball Mills? They provide an intimate mixture of the various components, which is essential for the final product's structural integrity, color, and thermal properties.
Example: A pottery manufacturer uses a ball mill to blend clay, flint, and feldspar into a smooth, consistent slurry that can be cast into molds to create ceramic tiles.
Other Notable Industries
Agriculture: Used for grinding fertilizers and pesticides to ensure even distribution.
Food Processing: Certain food powders and colorants are ground using ball mills, though often with strict hygiene standards.
Advanced Materials: Production of nanomaterials, superconductors, and metal powders for 3D printing (additive manufacturing) often relies on high-energy ball milling.
From the metals in our smartphones to the walls of our homes and the medicines we rely on, grinding ball mills are an invisible yet integral part of modern life. Their versatility, reliability, and ability to achieve precise results make them a cornerstone technology across a vast spectrum of industries. Understanding their applications highlights their critical role in transforming raw materials into the essential products that power our world.