Ball Coal Mill: Efficient Grinding for Power Plants & Industries
Introduction
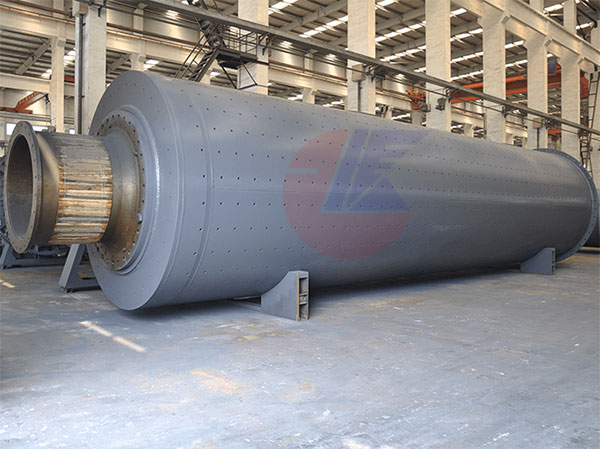
A ball coal mill (or coal ball mill) is a critical piece of equipment in coal-fired power plants and cement industries, designed to grind coal into fine powder for efficient combustion. This grinding process ensures optimal fuel efficiency, reduced emissions, and consistent thermal performance.
In this guide, we'll explore:
✔ How a ball mill for coal grinding works
✔ Key advantages over other coal pulverizers
✔ Industrial applications
✔ Maintenance & optimization tips
How Does a Ball Coal Mill Work?
A ball coal mill operates by rotating a horizontal cylinder filled with steel balls that crush and grind coal into fine particles. The ground coal is then dried and transported to burners for combustion.
Key Components:
Grinding Chamber – Contains coal and grinding media (balls).
Steel Balls – Crush coal through impact and attrition.
Classifier – Separates fine coal from coarse particles (in dynamic mills).
Hot Air Supply – Dries coal while grinding (critical for preventing clogging).
Discharge System – Delivers pulverized coal to burners.
Grinding Process:
Raw Coal Feeding – Coal enters the mill via a screw feeder.
Grinding Action – Rotating balls crush coal into fine powder.
Drying & Transport – Hot air dries and carries pulverized coal to the burner.
Rejection of Coarse Particles – Unfit particles are returned for regrinding.
Advantages of Using a Ball Coal Mill
Compared to vertical roller mills (VRMs) and hammer mills, a ball coal mill offers:
✅ Higher Grinding Efficiency – Produces uniform particle size for better combustion.
✅ Handles High Moisture Coal – Hot air flow prevents clogging.
✅ Lower Maintenance – Fewer wear parts than impact-based mills.
✅ Proven Reliability – Long operational lifespan in power plants.
✅ Flexibility – Works with various coal types (bituminous, lignite, anthracite).
Applications of Ball Coal Mills
1. Coal-Fired Power Plants
Grinds coal for pulverized coal combustion (PCC).
Ensures high thermal efficiency and low unburned carbon.
2. Cement & Steel Industries
Used for coal grinding in kiln firing and blast furnaces.
Provides consistent heat supply for clinker production.
3. Chemical & Industrial Boilers
Supplies pulverized coal for steam generation.
Types of Ball Coal Mills
| Type | Description | Best For |
|---|---|---|
| Low-Speed Ball Mill (Tumbling Mill) | Traditional design, 15–25 RPM | Large power plants |
| Medium-Speed Ball Mill | 50–100 RPM, better efficiency | Mid-sized industries |
| High-Speed Attrition Mill | Uses smaller balls, higher RPM | Fine coal grinding |
| Dynamic Air-Swept Ball Mill | Integrated classifier for finer output | Modern power plants |
Key Selection Criteria for a Ball Coal Mill
1. Coal Type & Moisture Content
High-moisture coal → Requires stronger drying capacity.
Hard coal (anthracite) → Needs larger grinding balls.
2. Grinding Capacity (TPH)
Small plants: 5–20 TPH
Large power stations: 50–100+ TPH
3. Energy Efficiency
Variable-speed drives reduce power consumption.
Optimized ball loading improves grinding efficiency.
4. Maintenance & Durability
High-chrome steel balls resist wear.
Easy-access liners reduce downtime.
Optimizing Ball Coal Mill Performance
1. Improve Grinding Efficiency
Optimize ball size & filling ratio (25–35% of mill volume).
Control air-to-coal ratio for better drying.
2. Reduce Power Consumption
Use high-efficiency classifiers.
Install variable frequency drives (VFDs).
3. Prevent Common Issues
| Problem | Solution |
|---|---|
| Excessive vibration | Check bearing alignment, balance grinding media |
| Low fineness output | Adjust classifier, replace worn balls |
| Coal buildup | Increase hot air temperature, clean mill regularly |
Future Trends in Coal Grinding Technology
AI-Based Optimization – Real-time adjustments for peak efficiency.
Hybrid Grinding Systems – Combining ball mills with roller presses.
Low-NOx Coal Mills – Reducing emissions through better combustion.
A ball coal mill remains a robust and efficient solution for coal grinding in power plants and heavy industries. Proper selection, maintenance, and optimization ensure high combustion efficiency, lower emissions, and reduced operating costs.
For long-term reliability, choose mills from reputed manufacturers and follow best practices in operation & maintenance.