The Comprehensive Guide to Ball Mill for Cement Grinding: Optimizing Efficiency and Performance
In the cement manufacturing industry, the ball mill for cement grinding plays a pivotal role in transforming raw materials into the fine powder that is essential for producing high-quality cement. As one of the most widely used grinding machines, the ball mill is critical for achieving the desired particle size and consistency in cement production. This article explores the importance of ball mills in cement grinding, their working principles, benefits, and best practices for optimizing their performance. Whether you're a plant manager, engineer, or industry professional, this guide will help you understand how to maximize the efficiency of your ball mill for cement grinding.
What is a Ball Mill for Cement Grinding?
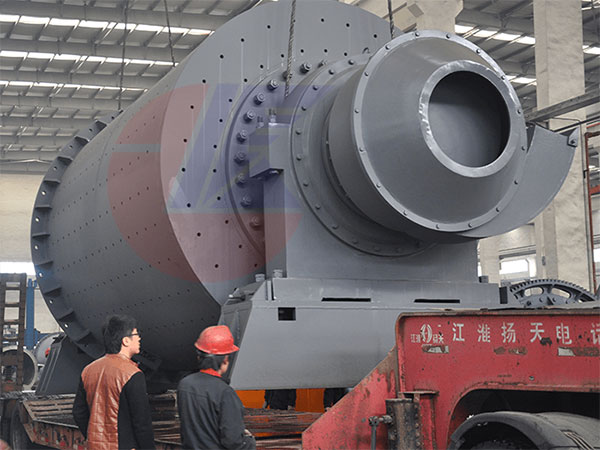
A ball mill is a cylindrical device used to grind materials such as clinker, gypsum, and other raw materials into fine powder. In the context of cement production, the ball mill is a key piece of equipment that grinds the clinker (produced by heating limestone and clay) and gypsum to produce cement. The ball mill operates by rotating a hollow cylinder filled with grinding media (usually steel balls) that cascade and impact the material, reducing it to the desired fineness.
Key Components of a Ball Mill for Cement Grinding
Cylindrical Shell: The outer structure that houses the grinding media and material.
Grinding Media: Steel balls or other materials that grind the clinker and gypsum.
Drive System: Includes the motor, gearbox, and bearings that rotate the mill.
Liners: Protective layers inside the mill to reduce wear and tear.
Feed and Discharge System: Allows raw materials to enter and exit the mill efficiently.
Separator: Classifies the ground material, ensuring the correct particle size distribution.
How Does a Ball Mill Work in Cement Grinding?
The ball mill for cement grinding operates on a simple yet effective principle:
Loading: The clinker, gypsum, and other additives are fed into the mill.
Rotation: The cylindrical shell rotates, causing the grinding media to cascade and impact the material.
Grinding: The material is ground into a fine powder through repeated impact and attrition.
Discharge: The ground cement is discharged and sent to storage silos for packaging and distribution.
The efficiency of the grinding process depends on factors such as the speed of rotation, the size and type of grinding media, and the material feed rate.
Benefits of Using a Ball Mill for Cement Grinding
High Efficiency: Ball mills are capable of grinding large quantities of material with relatively low energy consumption.
Consistency: Produces uniform particle size, which is critical for the quality of cement.
Versatility: Can handle a wide range of materials, including clinker, gypsum, and additives.
Durability: Designed to withstand the harsh conditions of cement production.
Scalability: Available in various sizes to meet the needs of small and large-scale cement plants.
Applications of Ball Mills in Cement Production
Clinker Grinding: The primary application of ball mills in cement plants is grinding clinker into fine powder.
Gypsum Grinding: Gypsum is added to control the setting time of cement.
Blended Cement Production: Ball mills are used to grind and blend supplementary cementitious materials (SCMs) such as fly ash, slag, and pozzolans.
Raw Material Grinding: In some cases, ball mills are used to grind raw materials before they are fed into the kiln.
Tips for Optimizing Ball Mill Performance in Cement Grinding
Optimal Loading of Grinding Media: Ensure the mill is filled with the correct amount and size of grinding balls. Overloading or underloading can reduce efficiency.
Control Rotation Speed: Operate the mill at the optimal speed to maximize grinding efficiency. Too fast or too slow can lead to poor performance.
Regular Maintenance: Inspect and maintain the mill regularly to prevent unexpected downtime. This includes checking liners, drive systems, and lubrication.
Proper Material Feed Rate: Control the feed rate to ensure consistent grinding. Overfeeding can cause clogging, while underfeeding reduces throughput.
Use of Grinding Aids: Additives such as glycols or amines can improve grinding efficiency and reduce energy consumption.
Monitor Particle Size Distribution: Use separators and classifiers to ensure the ground material meets the desired specifications.
Common Challenges in Cement Ball Mill Operations
Wear and Tear: The abrasive nature of clinker and grinding media can cause significant wear. Regular inspection and timely replacement of liners and grinding balls are essential.
Overheating: High temperatures can damage the mill and reduce efficiency. Ensure proper ventilation and cooling systems are in place.
Energy Consumption: Ball mills are energy-intensive. Optimizing operating parameters and using energy-efficient technologies can reduce costs.
Noise Pollution: Ball mills can generate significant noise. Use soundproofing materials and ensure the mill is properly balanced to minimize noise levels.
Future Trends in Ball Mill Technology for Cement Grinding
Automation and Digitalization: The integration of IoT and automation technologies allows for real-time monitoring and control of ball mill operations, improving efficiency and reducing downtime.
Energy-Efficient Designs: Manufacturers are developing ball mills with lower energy consumption and higher grinding efficiency.
Advanced Materials: The use of high-performance materials for liners and grinding media enhances durability and reduces maintenance costs.
Sustainability: Cement plants are increasingly focusing on sustainable practices, such as using alternative fuels and reducing carbon emissions during grinding.
Why Choose a Ball Mill for Cement Grinding?
The ball mill remains the preferred choice for cement grinding due to its reliability, efficiency, and ability to produce high-quality cement. Its versatility and scalability make it suitable for both small and large-scale cement plants. By optimizing operating parameters and adopting best practices, cement manufacturers can maximize the performance of their ball mills, ensuring consistent product quality and reducing operational costs.
The ball mill for cement grinding is an indispensable piece of equipment in the cement manufacturing process. Its ability to grind clinker and gypsum into fine powder with high efficiency and consistency makes it a critical component of cement production. By understanding the working principles, benefits, and optimization techniques, cement plant operators can ensure their ball mills operate at peak performance.
Investing in a high-quality ball mill and adhering to best practices will not only improve your cement production process but also contribute to long-term cost savings and operational efficiency. Stay ahead of the competition by leveraging the latest advancements in ball mill technology and adopting sustainable practices in your cement grinding operations.
By following this guide, you can make informed decisions about your ball mill for cement grinding, ensuring it meets your specific needs and delivers optimal results. Whether you're upgrading an existing mill or investing in a new one, this comprehensive guide will help you achieve success in your cement production process.